 현대제철 통합보고서
현대제철 통합보고서
Environment
Protecting Biodiversity3.2.5
Hyundai Steel minimizes its impact on the marine ecosystems near its steelworks and business sites by monitoring ecotoxicity and managing its wastewater treatment facilities. We are committed to reducing our emissions of water pollutants and improving the aquatic ecosystems of our local communities.
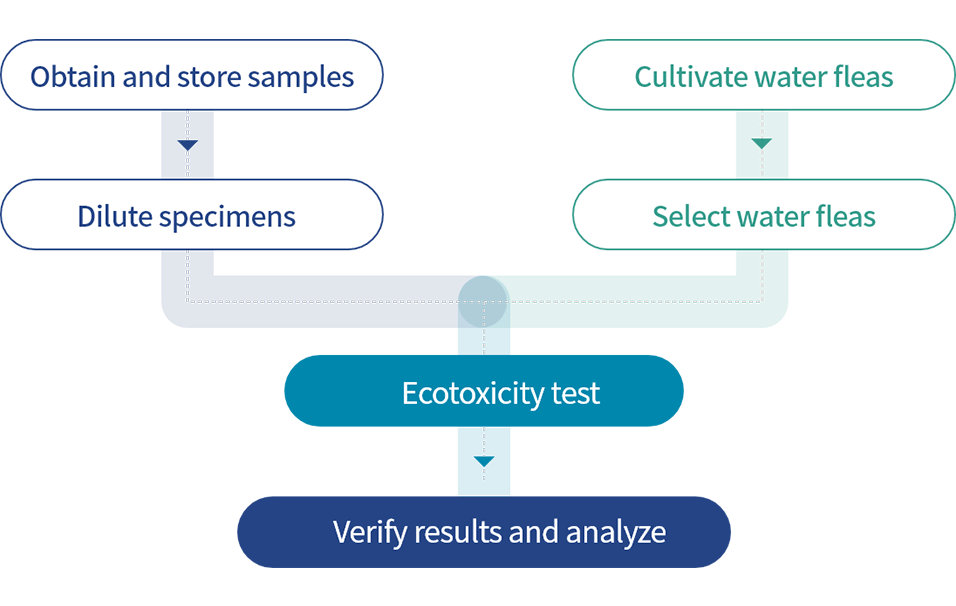
Monitoring Ecotoxicity
Since 2010, Hyundai Steel has been monitoring ecotoxicity to minimize the impact on aquatic ecosystems from the wastewater discharged directly into the ocean from our sites. We have independently established ‘work standards' for testing water quality that conform to the ‘heavy metal toxicity testing method using water fleas' as a standard method under Article 6 of the ‘Environmental Testing and Inspection Act'. These ecotoxicity assessments are conducted on a monthly basis. Also, we carry out annual independent risk assessment, and make efforts to improve the reliability of our testing processes. Furthermore, we operate a dedicated ecotoxicity testing lab where a constant temperature can be maintained and lighting can be adjusted, and we cultivate our own water fleas to ensure a stable supply for testing. In 2020, the ecotoxicity of wastewater discharged from the Dangjin Integrated Steelworks was below TU 1.01) thus meeting legal standards. Through these measures, we are able to systematically manage our wastewater treatment facilities to minimize the impact of the Danjin Integrated Steelworks on nearby marine ecosystems, thereby leading the way in protecting the biological diversity of aquatic ecosystems.
- 1) Legal standard: under TU 2
※ Refer to Standard Methods for Testing Water Quality
By-product Business Collaboration and Reporting System
Biodiversity Assessment Status
Hyundai Steel assesses ecological impact in the vicinity of our business sites, including the Dangjin Steelworks(785.5 hectares), our largest business site, as part of our continuous efforts to manage the ecosystem. The ecological impact assessment focuses on the air environment(air quality), water environment(surface/underground water quality), land environment(soil), and living environment(noise, vibration, waste). In 2020, we conducted quarterly assessments that formed the basis for establishing and implementing action plans to improve environmental facilities with the goal of minimizing our impact on the ecosystems near our business sites.
In order to preserve these ecosystems, we monitor the number and population of species(mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, fish, insects, land plants, seaweeds, etc.) that inhabit the areas near our business sites, including three types of legally protected species2). We also plan to establish and implement a plan to build an ecological park by 2022, which will include green areas to protect wildlife habitats. In addition, we are striving to disclose environmental issues to the public. For example, we opened the “Environmental Issues Reporting Desk” to collect opinions from local residents, and are operating the “Environment Improvement Council” through public-private sector cooperation.
In order to preserve these ecosystems, we monitor the number and population of species(mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, fish, insects, land plants, seaweeds, etc.) that inhabit the areas near our business sites, including three types of legally protected species2). We also plan to establish and implement a plan to build an ecological park by 2022, which will include green areas to protect wildlife habitats. In addition, we are striving to disclose environmental issues to the public. For example, we opened the “Environmental Issues Reporting Desk” to collect opinions from local residents, and are operating the “Environment Improvement Council” through public-private sector cooperation.
- 2) Kestrel (Natural Monument No. 323-8), Big Goose (Endangered Wildlife Class Ⅱ), Black-headed Plover (Natural Monument No. 326, Endangered Wildlife Class Ⅱ)
Population of wildlife near the Dangjin Steelworks
(as of 2020)
| Category | Mammals | Birds | Amphibians, reptiles |
Freshwater fish | Insects | Land plant | Plankton |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of animals (species) | 10 | 57 | 9 | 3 | 78 | 251 | 117 |
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.

