 현대제철 통합보고서
현대제철 통합보고서
Performance
Performance
Materiality Assessment3.1
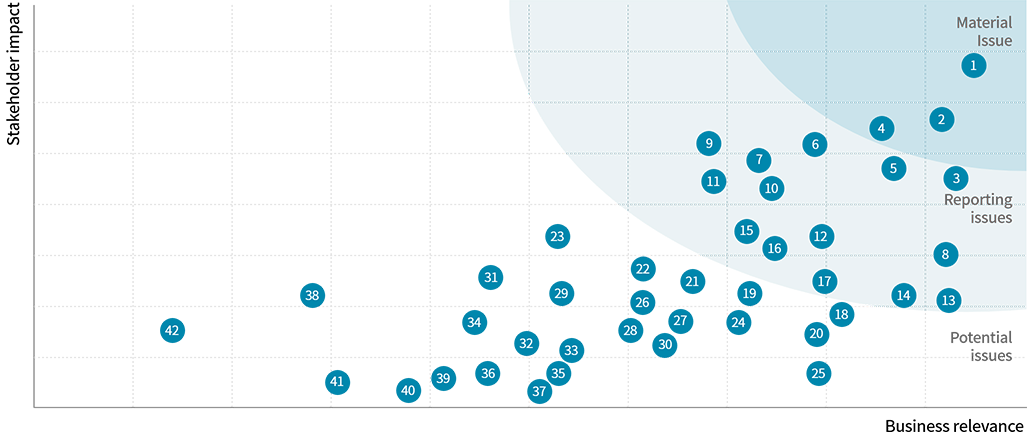
Materiality Assessment Process
Hyundai Steel has evaluated a range of issues in terms of their 'business relevance' and 'stakeholder impact', considering the company's situation and the characteristics of the steel industry, in order to identify key issues related to sustainability. We first identified issues with a high 'business relevance' by conducting an internal employee survey and analyzing competitor trends. We prioritized issues with high 'stakeholder impact' through a combination of external stakeholder surveys, media reports and matters raised by international organizations. Among them, key issues were selected through discussion with relevant departments and confirmation by the management. These key issues are also considered from the perspective of their financial impacts such as cost, revenue and risk.
Step 1. Issue Pool Formation
In terms of sustainability, 42 material issues were identified through a comprehensive analysis of global standards and initiatives, external evaluation requirements and stakeholder impact, while taking into consideration the internal/external environment of Hyundai Steel and its stakeholders.
- Trends in international standards: Analysis of international standards and assessment indicators, including GRI Standards, ISO 26000, DJSI, SDGs
- Global benchmarking: Survey of 11 business issues and trends covering leading companies in sustainability management, comparable companies, etc.
- Media research: Survey of 1,996 media articles appearing from January 2020 to January 2021
Step 2. Materiality Assessment
We conducted a materiality assessment of the issues in consideration of business relevance and stakeholder impact, including surveys of internal and external stakeholders, media research, global benchmarking and international standards.
- Business relevance: Relevance to steel industry, aligned with mid- to long-term strategy
- Stakeholder impact: Issues of interest to stakeholders, legal and regulatory compliance, sustainability-related ESG trends
Step 3. Selection of Key Issues
We identified key issues that are in alignment with economic, environmental and social indicators as defined by the GRI Standards. In addition, we present Hyundai Steel's response strategies, specific actions, key performance and targets.
Material Topics in Integrated Report
Key Issues
The attributes of potential impacts are classified by cost, revenue and risk.
| Key Issue | Reason | Impact on Stakeholders | Impact Attributes1 | Scope of Reporting |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reduce the emission of environmental pollutants | The steel industry is perceived as the industry that produces the largest volume of GHG emissions and, moreover, social interest in managing environmental pollutants is on the rise. In response, the government is amending related legislation to strengthen corresponding regulations and measures. | Employees, suppliers, local communities and government | Cost | Pollutant Management |
| Strengthen worksite health and safety | Occupational hazards not only reduce productivity, but also represent potential risks and can seriously impact business operations. Steel production exposes the surroundings to high temperatures, high pressure and toxic gases. Furthermore, extremely heavy coils are used, resulting in extreme danger if accidents occur. | Customers, employees and suppliers | Risk | Occupational Health and Safety |
| Expand supply chain ESG management | If issues such as environmental hazards, human rights violations, or ownership abuses are identified at our major suppliers and exposed in the media, business risks that can damage our reputation may arise. In addition, as more client companies now demand the results of supply chain ESG assessments, the transaction risk arising from supply chain ESG is increasing. | Suppliers and local communities | Risk | Supply Chain Management |
| Strengthen product competitiveness through R&D | Global steelmakers are enhancing their competitiveness in the market through the expansion of contact points with customers and convergence with the latest material and IT technologies. In particular, the development of new products and production technologies that reflect the needs of related, major industries, such as automobile, construction and shipbuilding, is gaining greater importance as an element of sustainable growth. | Executives, customers, shareholders and investors | Revenue | R&D Performance |
| Enhance legal compliance | Recently, in addition to the pursuit of profit, there have been increasing demands on the social responsibility and role of companies. Accordingly, their legal, ethical, social, and environmental responsibilities are now being emphasized. By fulfilling ethical responsibilities, businesses are making efforts to earn trust from all stakeholders, including customers, shareholders, employees, competitors, and suppliers. | Customers, employees, suppliers and government | Risk | Ethical Management |
Strategies for responding to key issues
1. Reduce emission of environmental pollutants
Across our management activities, Hyundai Steel strives to minimize the environmental impact of our production processes. In order to reduce pollutants, we have installed three air pollutant reduction facilities in the Dangjin Integrated Steelworks, and reduced air pollutant emission by more than 65% compared to that of 2016, exceeding our reduction target.
Key performance
- Reduce air pollutant emissions
- · 2019: 18,131 tons
- · 2020: 8,116 tons
Target
- Reduce air pollutant emissions to 50%(10,297 tons) or below, compared with a 2016 baseline year
- (to be achieved by 2021)
- Our existing emissions target was increased in line with the revised Air Quality Conservation Act, which expanded the range of facilities subject to emission control. The target value is set in accordance with internal criteria.
2. Strengthen health and safety on worksites
As part of our continuous efforts to enhance safety across our business sites, Hyundai Steel has acquired KOSHA 18001 and ISO 45001 certifications for our safety and health management system. In addition, we have been implementing our planned investment of KRW 300 billion in safety management across three years since 2019. We also identify areas to improve safety across all our business sites, prepare comprehensive measures for improvement and report the result to the management.
Key performance
- TRIFR
- (Total Recordable Injury Frequency Rate)
- · 2019: 3.72
- · 2020: 3.01
Target
- TRIFR Target: Zero
- (By 2025)
- Refer to 4.2 Social Performance "Occupational Disasters Rate" for details of TRIFR
3. Expand supply chain ESG management
Hyundai Steel adopted integrated supply chain management as a key business strategy by incorporating supply chain ESG management. Accordingly, we have built a supply chain management process and conduct risk assessments of 350 suppliers annually. Among these, the bottom 5% are classified as high-risk suppliers, for which we conduct on-site due diligence and implement improvement measures.
Key performance
- 1. Supply chain ESG assessment ratio
- · 2019: 32%, 2020 : 36%
- 2. Purchasing manager ESG training ratio
- · 2019: 55%, 2020 : 100%
- 3. Average score in the supply chain ESG assessment
- · 2019: 67 points, 2020 : 64 points
Target
- 1. Supply chain ESG assessment ratio 35%(to be achieved by 2023)
- 2. Purchasing manager ESG training ratio 80%(to be achieved by 2023)
- 3. Average score in the supply chain ESG assessment 80 points(to be achieved by 2023)
- The supply chain ESG assessment ratio is measured on the basis of the accumulated number of assessed suppliers during the three-year period. Refer to ‘3.3.4 Supply Chain Management’ for detailed information on Supply Chain ESG.
4. Strengthen product competitiveness through R&D
With an eye towards the future, Hyundai Steel focuses on R&D such as the development of eco-friendly technologies to achieve carbon neutrality, and next-generation mobility materials. We also conduct R&D to secure our capability to achieve sustainable growth - for example, through the expansion of high-profit new steel types and profit-oriented process technologies. In this manner, we are rapidly responding to changes in the market and society and maintaining a harmonious balance between new products, process technology, and environmental technology. We are also expanding our supply capabilities by developing new steel types for automotive steel sheets, and expanding our customer base through non-face-to-face technology marketing for global customers. Going forward, we will continue to enhance our competitiveness in front and back office activities through organic alignment and coordination with our business strategies.
Key performance
- R&D investment costs
- · 2019: KRW 136,250 million
- · 2020: KRW 142,536 million
Target
- Lead global technology competitiveness, secure future mobility and energy material supply capabilities
- (to be achieved by 2025)
5. Enhancement of legal compliance
Hyundai Steel pursues fair and transparent competition based on ethics and morals, and is well aware that ethical management forms the fundamental basis of corporate competitiveness. In this regard, we strive to ensure ethical management is firmly rooted company-wide by producing guidebooks and promoting the Ethics Charter and Code of Conduct. In addition, ethics training is provided to all employees in order to share the standards of conduct to abide by when performing their duties. Through these efforts, a fair and transparent relationship is maintained with our stakeholders.
Key performance
- Compliance training training (fair trade, ethical management, overseas anti-corruption law, etc.)
- · 2020: 481 persons
Target
- Establish a compliance management system, based on legal risk analysis, by sector
- (to be achieved by 2025)

