Response to Climate Change
In response to climate change, Hyundai Steel is making a range of efforts across all business operations, such as GHG reduction activities. In line with Korea's NDC roadmap, the Company takes active response measures, introducing new facilities and improving the existing processes, to reduce energy consumption and GHG emissions.
Climate Change Governance
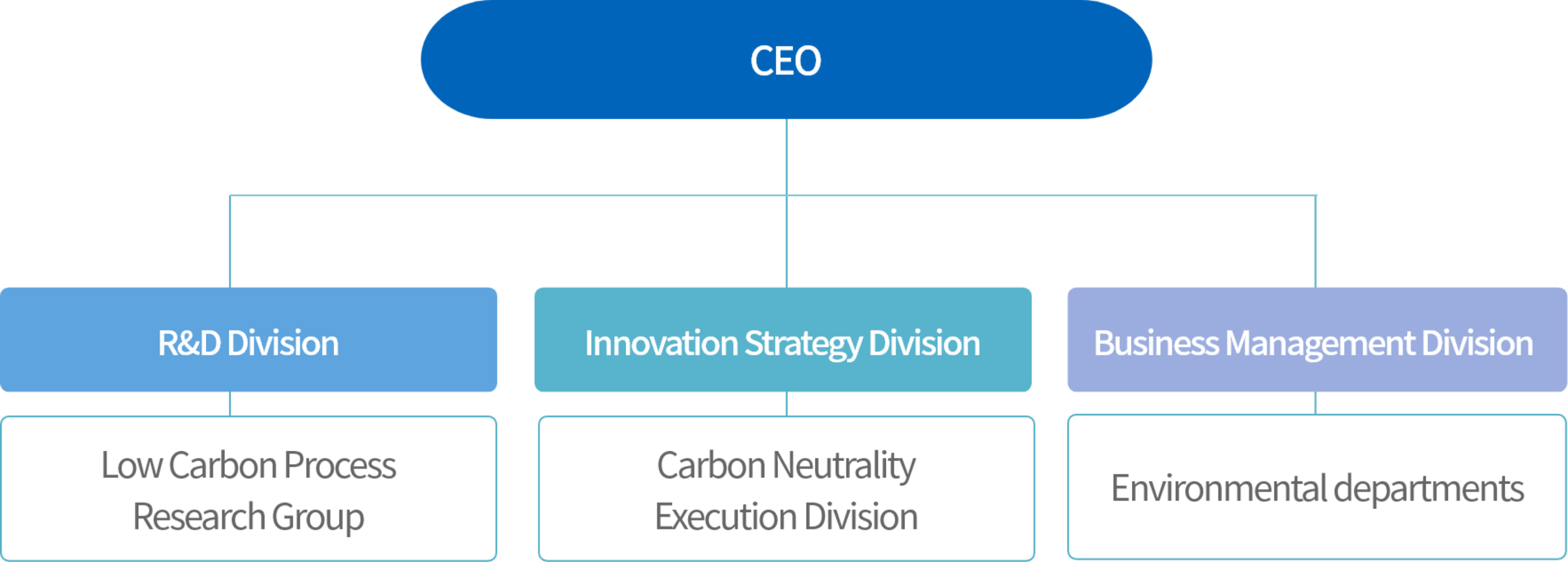
In line with global efforts to respond to climate change, the Korean government declared to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050, and revised upward1) Korea's NDC(Nationally Determined Contribution) to 40% or more GHG emission cut by 2030, compared to the 2018 level. As increasing attention to carbon neutrality has been putting pressure for the transformation of the global steel industry at home and abroad, Hyundai Steels responded by re-organizing the company structure and strengthening the climate change counter response system. February 2021, the Low Carbon Process Research Group was newly established in the R&D Division with specialized researchers. In January 2022, the Carbon Neutrality Execution Division was launched under the Innovation Strategy Division in order to strengthen our governance system responding to climate change. The Carbon Neutrality Execution Division is a control tower establishing carbon neutrality strategies and studying a transition to a carbon neutral production system, thus serving as a bridge connecting carbon neutral technologies and production.
Further, we take climate change as a key issue of sustainable management and are responding at a company level through the ESG governance system(ESG Administrative Council – ESG Directors' Council- Transparent Management Committee). Carbon emission is added to the key management targets of major executives as part of our efforts to enhance responsible management for carbon neutrality. The BOD overseas our corporate response to climate change, reviewing strategies and risk management policies and providing guidance, monitoring progress on targets, and making decisions on ESG-related matters through the Transparent Management Committee. The management receives regular reports on results of our measures on greenhouse gas, energy, and environmental issues, and makes investment decisions considering our climate change strategies, reduction targets, and risk management.
- 1) previous NDC by 2030: 26.3% reduction compared to the 2018 level
Goals and Strategies for Carbon Neutrality
As a move to meet carbon emission reduction requirement under the NDC target of the government, Hyundai Steel has set a goal of minimizing carbon costs through optimal reduction of company-wide carbon emissions and established a two-route strategy. The essence of our strategy is to reduce carbon footprint using our best know-how related to electric arc furnace, and to establish a carbon-neutral manufacturing system for automobile steel products by introducing Hy-Arc.
Route 1 is to achieve 'Carbon-neutral Production Process' aimed at minimizing risks associated with technology, facility, investment, and profit. The Company will improve processes, use low-carbon raw materials, and make an energy transition in phases so as to control our emissions in line with the government's NDC target. Route 2 is 'Low Carbonization of Products' using electric arc furnaces, so that we can make timely responses to the trade barrier of CBAM (Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism) and customers' demands. For this, Hyundai Steel introduced a new low-carbon steel manufacturing system named 'Hy-Cube' and is implementing a mid- to long-term technology roadmap. Based on this two-route strategy, Hyundai Steel will establish and implement detailed action plans and achieve carbon neutrality by 2050.

-
Carbon-neutral Production Process
- · Reduce carbon emissions from processes
- · Use low-carbon raw materials
- · Shift to renewable energy
Route-
Short-term process improvement2025
-
Application of low-carbon raw material technology2030
-
Energy transition2040
-
Transition to Hy-Arc2050
-
Carbon neutrality
-
Low Carbonization of Products
- · Establish a low-carbon product supply strategy
- · Cooperate with advanced overseas companies
- · Review technology for carbon-neutrality transition
Route-
Element technology development, facility engineering2024New facilities installation
-
Hy-Arcstart-upAutomobile steel plate development
(to be determined)
HBI technology -
Low-carbonHydrogen-based ironmaking(HBI)
steel plate2030
Use of renewable energy -
Carbon-neutral
steel sheet2040
2050 Joint Declaration of Carbon Neutrality by the Steel Industry
In February 2021, six steel companies, including Hyundai Steel, made a joint declaration to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050 and launched the 'Green Steel Committee', which is composed of industry, academia, research institutes, and government ministries. Accordingly, we plan to develop new technologies(hydrogen based ironmaking), reduce carbon emissions by making transformation in the production system, share information, develop policy tasks, and strengthen international cooperation.
Climate Change Risk Identification and Assessment Process
Hyundai Steel has been operating the Carbon Neutrality Task Force since 2021 in order to cope with climate change issues. Through environment and energy meetings, the Task Force has identified key issues to manage across the environment and energy sectors in response to drastic government policy changes and demand for ESG management, quantified risks, and set directions for strategic responses. Based on these efforts, CFT was organized for each sector, such as technology, production, operation/management, policy, and business strategy, developed and managed short-term tasks to achieve the carbon emission reduction targets by 2030, established mid- to long-term strategies and responded to government policies.
Climate change strategy
Mid-Long term risks and opportunities
| Type of risk | Risks | Opportunities | Goals | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transition Risks | Policy and Legal |
|
|
Long term |
| Technology |
|
Long term | ||
| Market |
|
|
Mid term | |
| Reputation |
|
|
Long term | |
| Physical Risks | Acute |
|
|
Mid term |
| Chronic |
|
|
Long term | |
Review of Scenarios
Transition risk: review changes in domestic/overseas policies and markets and their impact on our securing technology competence based on scenarios, such as the 2050 Long-term Low Greenhouse Gas Emission Development Strategies(LEDS) of Korea and the Net-Zero Emissions by 2050(NZE) of International Energy Agency(IEA).
Physical risk: review impact of temperature rise and natural disasters on facilities and supply chain, on the basis of the Representative Concentration Pathways(RCP) scenario of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change(IPCC) report and internal scenarios set by the Company
Response to Transition Risks
In April 2022, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change(IPCC) held the 56th general assembly and adopted a report calling for 43% net GHG reduction by 2030 and 84% by 2050, compared with the 2019 levels, in order to keep global warming below 1.5°C. As a result, there will be increasing demand from the global community that the 2030 Nationally Determined Contribution(NDC) targets already set by countries should be raised further and more ambitious 2035 targets should be set in 2025.
Accordingly, Hyundai Steel established GHG reduction strategies to cope with Korea's NDC target as a move to make flexible responses to climate change. As laws and regulations on the carbon credit trading system are being tightened in Europe, we also checked on associated risks to our manufacturing and export, and have been taking measures to minimize these risks through investment in eco-friendly facilities and changing production processes.
Implementation of the Carbon Credit Trading System
The carbon credit trading system was introduced「the Act on the Allocation Trade of Greenhouse Gas Emissions」since 2015. Hyundai Steel was subject to carbon credit allocation and is preparing to comply with the Act in 2021, the first year of the 3rd planning period of the carbon credit trading system from 2021 to 2022. We hold internal energy meetings and carry out energy saving activities in the fields. In addition, we tap into paid allocation, market mechanism, and operate the GHG Reduction Task Force in order to remove risks associated with securing carbon credit. The Company also establishes a GHG reduction portfolio so as to comply with relevant laws and ease burdens from reduced carbon credit. The Company operates an IT-based system for the accurate and efficient management of GHG emissions through continuous consultations among relevant departments. We analyze the risk of GHG generation by calculating GHG emissions associated with fuels and raw materials across all business sites every month and consequent carbon costs. In addition, associated financial impact is also considered in reviewing products and new investments. As such, Hyundai Steel strives to reduce GHG emissions, develop domestic/overseas GHG reduction projects, and save energy in order to cope with the government's '2030 GHG Reduction Roadmap'.
Disclosure of Response to Climate Change
Through participation in the Carbon Disclosure Project(CDP) since 2012, Hyundai Steel has transparently disclosed to global financial investors and stakeholders its efforts to respond to climate change. Therefore, we received the sector leadership award in recognition of outstanding corporate response to climate change. Moreover, we publicly disclose information concerning our climate change-related activities in accordance with international standards(GRI Standards, SASB, WEF, TCFD, etc.) through our Integrated Report published every year. Furthermore, we plan to revise our CDP countermeasure and improve by receiving external consulting from 2022. In particular, we will examine our data disclosure for Scope 3 and improve data accuracy, and further promote transparency through external assurance.
Support for a Carbon-neutral Event of the Local Community
Hyundai Steel signed an agreement with Dangjin City in August 2021 to hold carbon-neutral events(e.g. the 200th anniversary of the birth of Father Kim Dae-geon) and has provided support.
For carbon-neutral events, greenhouse gas emissions from energy sources such as vehicles, electricity, and LNG used throughout the events are calculated and offset to 'zero' by using voluntary carbon credits(VCS) and thus fulfill a social responsibility for climate change mitigation.
At the event commemorating the 200th anniversary of Father Kim Dae-geon's birth, Dangjin City calculated greenhouse gas emissions generated from the event and Hyundai Steel offset the carbon emissions by donating VCS acquired through REDD 1) in the Amazon jungle, etc. This event was the first of its kind in Korea, conducted in accordance with the international standard for carbon neutrality(PAS 2060) through cooperation among a company, a local government, and a global assurance agency. Lloyd's Register, a global assurance agency, verified greenhouse gas emissions generated from the event and the amount offset by VCS to ensure the transparency of the carbon-neutral event.
 Assurance statement on the carbon neutrality event issued by Lloyd's Register of the UK
Assurance statement on the carbon neutrality event issued by Lloyd's Register of the UK
- 1) REDD(Reducing emissions from deforestation and forest degradation): a program managed by the United Nations, whereby developed countries reduce GHG emission by preventing the destruction and degradation of forests and pursue forestation in developing countries, and thus acquire incentives such as carbon credit.
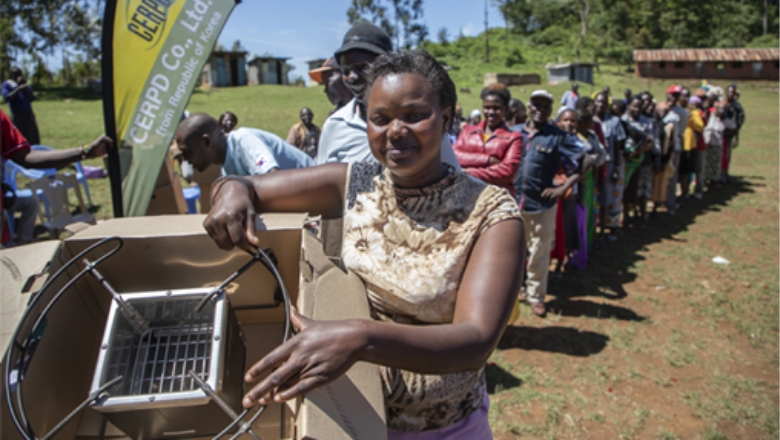
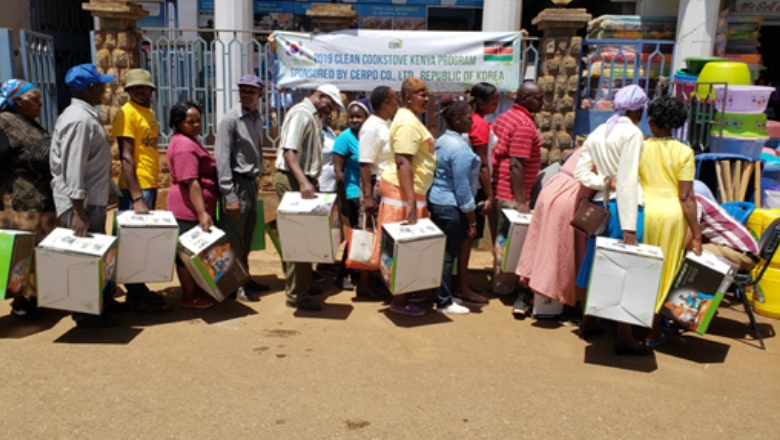
Securing Overseas Carbon Credit by Providing Cooking Stoves and Water Purifiers
Together with an overseas consulting firm, Hyundai Steel is engaged in a project to supply cooking stoves and water purifiers to some of the world's least developed countries, including Kenya, Myanmar and Bangladesh. Citizens in these countries burn a significant amount of firewood for their everyday needs, which generates black carbon. By providing cooking stoves, as a substitute for burning wood, and water purifiers, we are not only contributing to improvement in their quality of life, but also securing overseas carbon credits and reducing our carbon credit risk.


Review of TCFD Information Disclosure
Hyundai Steel is considering setting up a climate change management system and disclosing information as recommended by the TCFD(Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures), which is an international consultative organization established in 2015. This management system discloses four key sections outlined in the TCFD's recommendation--governance, strategy, risk management, and standards and targets—and elaborates our activities and efforts. With that, we aim to provide our stakeholders, including investors, with useful information to their key decision-making.

Transition to Zero-emission Vehicles(K-EV100)
In accordance with the K-EV100 Project1) by the Ministry of Environment, Hyundai Steel publicly announced to replace company vehicles to zero-emission vehicles and has since been reporting the process on a regular basis. Currently, Hyundai Steel plans to replace 336 vehicles in total(10 owned, 326 leased), out of which 10 were replaced with hydrogen vehicles in 2021 and eight including two EVs and six hydrogen vehicles in 2022. The replacement cost is subsidized by this project, and hence cost burdens associated with such replacement, GHG emission and carbon credit are expected to decrease in part.
- 1) K-EV100 Project: A project implemented by the Ministry of Environment, whereby companies publicly declare a transition to zero-emission vehicles in phases until 2030
Development of Low-carbon Raw Materials with Brazil's Vale
Amid increasing demand for carbon reduction worldwide, securing competitive, low-carbon raw materials is becoming ever more important. In order to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050, Hyundai Steel signed an MOU with Vale of Brazil, one of the world's top three mining companies in November 2021, to promote cooperation on GHG emission reduction and development of low-carbon raw materials, through which we will take steps closer to decreasing carbon emissions. A key part of this MOU is the feasibility study of iron ore briquettes, which are expected to be a low-carbon substitute for the future. Hyundai Steel is planning to review the feasibility of various low-carbon steel materials, such as iron ore briquettes, high-quality pellets, hot briquetted iron(HBI), and related technologies. Moving forward, we will maintain close cooperation with Vale, expanding the areas of cooperation across low-carbon iron sources and promoting technological cooperation to reduce carbon emissions in the steel industry.
Business Agreement with Dangjin City to Construct the RE100 Industrial Complex
In October 2021, Hyundai Steel signed a 'business agreement for the RE100 industrial complex construction project' with Dangjin City and Hyundai Green Development. The purpose of this project is to facilitate Dangjin's transition to renewable energy and activate the local economy by attracting businesses.
The RE100 industrial complex will be approximately 458,900㎡ in Gagok-ri, Songsan-myeon, near the Dangjin Integrated Steelworks, and is expected to be completed in 2023. Renewable energy supply infrastructure will be installed for a total capacity of 69.25MW, including solar energy(1.75MW) and biomass(10MW). By supporting the use of new renewable energy such as green premium system, renewable energy certificate (REC), and third party PPA (Power Purchase Agreement), we plan to improve corporate image, achieve carbon neutrality, and create jobs.
 Signing ceremony for the RE100 industrial complex construction project
Signing ceremony for the RE100 industrial complex construction project
MOU for Carbon-neutral Technology Cooperation with Korea Institute for Energy Research
On May 2022, Hyundai Steel signed a MOU with the Korea Institute for Energy Research(KIER) to promote technology collaboration for carbon capture and storage technology(CCUS), hydrogen production and energy efficiency improvement and lead the carbon neutrality of the steel industry. Our cooperation with the Korea Institute for Energy Research has continued since 2016, in the fields of greenhouse gas and energy for the purpose of creating a low-carbon manufacturing system. We newly entered into a MOU for energy and environment as carbon neutrality has recently emerged as a key issue to sustainable management. Under this MOU, Hyundai Steel plan to utilize the leading energy-related technologies of KIER in order to improve the performance of our steelworks facilities and optimize operation. In addition, we will accelerate technology development to realize carbon neutrality in the mid- to long-term, such as hydrogen production, CCUS, and carbon-free combustion, which are the basic technologies for creating green steel.
MOU for Technological Cooperation with Korea Institute of Geoscience and Mineral Resources for Low-carbon Raw Materials
Hyundai Steel entered into a MOU with the Korea Institute of Geoscience and Mineral Resources(KIGAM) on May 2022, for cooperation in optimal use of raw materials and development of operational technologies. Under this MOU, the Company established a strategic partnership related to carbon-neutral technology in the field of raw materials for steelmaking, and plans to actively introduce leading technologies related to mineral resources from KIGAM.
With that, we expect to speed up the development of technologies enabling us to operate low-carbon steel mills in the mid- to long-term, such as carbon-neutral raw materials, resource recycling, and raw material analysis technology, which are the basic technologies for 'green steel'. Utilizing KIGAM's recycling technologies, we also expect to add value to waste resources, and further reduce carbon and harmful substances emitted from using raw materials.
Response to Physical Risks
According to a report by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change(IPCC), sustained global warming caused by climate change will increase neutral disasters, such as heatwaves on land and at sea, floods, earthquakes, and tropical storms, and raise coastal sea levels. Through scenario analyses, Hyundai Steel is striving to preemptively identify such physical risks and develop effective countermeasures.
Advancement of Internal Management for Disaster Response
Due to the impact from climate change, the Korean Peninsula is dealing with damage caused by the increased frequency of typhoons.
Hyundai Steel has established the emergency response regulation for business sites, putting in place internal management procedures for employees' evacuation and facilities restoration and ensuring undisrupted, stable production despite a disaster.
In the event of a disaster, we check on time and cost required for restoring disrupted production infrastructure, such as manufacturing processes, disaster prevention facilities, and raw materials supply, and revenue lost to disrupted operation. We also periodically inspect and improve structures and check on facilities and equipment to prevent natural disasters. Further, we consider various sources of raw materials as a move to cope with raw materials supply disruption caused by natural disasters.
The Company is covered by the package insurance so as to minimize property damage caused by physical risks, as well as an environmental liability insurance to minimize damage of surrounding areas due to environmental accidents caused by facility destruction at our business sites.
Response to Natural Disasters
Hyundai Steel is putting in great effort to prevent safety accidents regarding high temperature and pressure caused by frequent temperature change. Separate standards for operation are established, with cooling relaxation facilities, tracking health condition of workers, and providing safety education. Additionally, each steelworks has in-house an emergency medical team and a fire-fighting team and conducts simulation drills.